This is the legacy documentation of Project-level Custom Applications, which is in maintenance mode. Visit the new documentation for Org-level Custom Applications.
Application config
This feature is available from version >= 16.15.0.
A Custom Application requires certain configuration to be able to work, for example which commercetools APIs should be used in which cloud region.
The configuration of a Custom Application is defined in a JSON file with one of the following names:
.custom-application-configrc.custom-application-config.<ext>custom-application-config.<ext>
The <ext> refers to the file extension chosen for the configuration file. See list of supported file extensions.
The file needs to be placed in the application root folder to be automatically loaded.
The application config is the new recommended replacement of the previous env.json and headers.json files. Read the release notes on how to migrate to the new config.
File format
The configuration is written as JSON and follows a strict JSON schema, which is part of the application-config package. The JSON schema is also used to validate the configuration file when starting the Custom Application.
The configuration file only requires a minimal set of information and from that it can infer all the necessary data.
{"name": "Avengers app","entryPointUriPath": "avengers","cloudIdentifier": "gcp-eu","env": {"production": {"url": "https://avengers.app"}}}
Configuration properties
In the example above, you can see all the necessary properties that are required to have a minimal configuration.
You can also inspect the JSON schema to see all available properties.
This is a list of all important properties and how they can be used:
entryPointUriPath
The entryPointUriPath refers to the unique route path of the Custom Application. This is the identifier that the Merchant Center Proxy uses to match the HTTP request and to forward it to the Custom Application URL. This value also needs to be used in the application client side routes.
Furthermore, this value must be the same as the Application route path when registering the Custom Application.
For example, if the Custom Application should be served at the route /:projectKey/avengers, the entryPointUriPath must be set to avengers and the same for the application routes.
<Switch><Routepath="/:projectKey/avengers"component={ApplicationRoutes}/>{/* Catch-all route */}<RouteCatchAll /></Switch>
cloudIdentifier
The cloudIdentifier is an enum of pre-defined values that map to the supported cloud regions.
env
The env object represents different environments (for example production). The environment used depends on the environment variable MC_APP_ENV. If MC_APP_ENV isn't set then NODE_ENV will be used. If neither is set it defaults to development.
The MC_APP_ENV is useful if you want to run the production build of the Custom Application locally. In this case the NODE_ENV needs to be set to production. However, because the application runs locally, you need to have the URL references pointing to localhost, thus the MC_APP_ENV needs to be set to development.
env.production.url
The url is the full URL value where the Custom Application runs in production. This value is also used to configure the Content Security Policy (CSP) HTTP headers to allow the browser to request data from the application domain.
env.production.cdnUrl
The cdnUrl is the full URL value where the Custom Application static assets are hosted, like an external CDN. If the static assets are hosted alongside the Custom Application, you can omit this option and the Custom Application url will be used instead.
additionalEnv
The additionalEnv is an object that should be used to specify properties unique to your Custom Application. These properties are then made available to the runtime application environment.
For example, if the Custom Application should reference an external API, or have links to certain support pages, etc.:
{"name": "Avengers app","entryPointUriPath": "avengers","cloudIdentifier": "gcp-eu","env": {"production": {"url": "https://avengers.app"}},"additionalEnv": {"trackingSentry": "https://000@sentry.io/000","avengersSupportUrl": "https://support.avengers.app"}}
headers
The headers object contains configuration for csp (Content Security Policy (CSP)) and featurePolicies (Feature Policy).
The required Content Security Policy (CSP) headers are inferred by default from the cloudIdentifier and the env.production.url. This includes the hostname where the Custom Application is hosted and the hostname of the Merchant Center API Gateway.
headers.csp
The csp object can be used to define additional settings for the following directives:
connect-srcfont-srcimg-srcscript-srcstyle-src
headers.featurePolicies
The featurePolicies object can be used to configure the HTTP Feature-Policy header.
headers.permissionsPolicies
The permissionsPolicies object can be used to configure the HTTP Permission-Policy header.
Supported file extensions
The following file extensions for the application config are supported: .json, .js, .cjs, .mjs, .ts.
The file extensions .js, .cjs, .mjs, .ts are only supported from version >= 20.9.0. These can be used in cases where the information you need to provide must be imported from another file, for example a constants file or something similar.
For example:
const { entryPointUriPath } = require('./constants');const name = 'Test application';/*** @type {import('@commercetools-frontend/application-config').ConfigOptions}*/const config = {name,cloudIdentifier: 'gcp-eu',entryPointUriPath,env: {production: {url: '${env:APP_URL}',},},};module.exports = config;
const entryPointUriPath = 'test';module.exports = { entryPointUriPath };
Using variable placeholders
Variable placeholders are a way of injecting certain information into the "static" configuration file.
Environment variable references
To make the application config more reusable across different environments, you can use references to environment variables within the JSON file.
References are specified with a special expansion-like syntax ${} together with the prefix key env:. For example, to load an environment variable called APP_URL, you would use ${env:APP_URL}.
Imagine developing a Custom Application that can be used in the commercetools platform Europe region and North America region. We can assign the ${env:CLOUD_IDENTIFIER} reference to the field cloudIdentifier and pass the actual value using environment variables.
{"cloudIdentifier": "${env:CLOUD_IDENTIFIER}"}
The CLOUD_IDENTIFIER environment variable can be provided in various ways.
For example:
as an inline environment variable when running a script command
CLOUD_IDENTIFIER=gcp-eu mc-scripts startusing a dotenv file
.env-euTerminalCLOUD_IDENTIFIER=gcp-eumc-scripts --env .env-eu startby defining the environment variables in your CI service
You can also pass multiple references to the same value:
{"additionalEnv": {"authorityUrl": "https://${env:IDP_URL}/${env.IDP_ID}"}}
Intl message references
This feature is available from version >= 20.8.0.
References for Intl messages are specified with a special expansion-like syntax ${} together with the prefix key intl:. For example, to load a translation message from the en.json file named Menu.Avengers, you would use ${intl:en:Menu.Avengers}.
This is useful when specifying menu link labels, for example:
{// ..."menuLinks": {// ..."defaultLabel": "${intl:en:Menu.StateMachines}","labelAllLocales": [{"locale": "en","value": "${intl:en:Menu.StateMachines}"},{"locale": "de","value": "${intl:de:Menu.StateMachines}"}]}}
The reference placeholder assumes that the Custom Application has the translation files in one of the following locations:
<app_root>/src/i18n/data/<locale>.json<app_root>/i18n/data/<locale>.json
Runtime application environment
Based on the application config, the necessary information for the Custom Application for runtime usage are injected into the global variable window.app.
This value must be used in the <EntryPoint> component when rendering the <ApplicationShell>.
const EntryPoint = () => (<ApplicationShellenvironment={window.app}// other props/>);
The environment prop is parsed and injected into a React Context, making it available to the entire application. To access it, use the @commercetools-frontend/application-shell-connectors package.
import { useApplicationContext } from '@commercetools-frontend/application-shell-connectors';const MyComponent = () => {const applicationName = useApplicationContext(context => context.environment.applicationName);return (<div>{`Welcome to the application ${applicationName}!`}</div>);};
All the properties defined in the additionalEnv object are made available to the context.environment object.
Editor support
To facilitate the usage of the application config, you should instruct your editor to provide hints and code completion (IntelliSense) depending on the format of the configuration file.
JSON Schema support for VSCode
When using JSON files, you can take advantage of the JSON schema for the application config. To enable JSON schema autocompletion and validation support, add a reference to the schema.json URL in the VSCode settings (either user settings or workspace settings):
"json.schemas": [{"fileMatch": ["/.custom-application-configrc","/.custom-application-config.json","/custom-application-config.json"],"url": "https://docs.commercetools.com/custom-applications/schema.json"}]
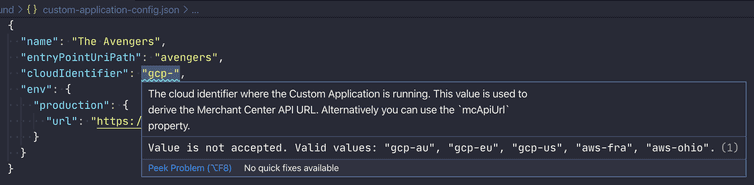
Other editors might have different settings.
Using JSDoc @type expression
For non-JSON files, you can annotate the configuration object with a JSDOc @type tag, pointing it to the exported TypeScript declaration of the @commercetools-frontend/application-config package.
/*** @type {import('@commercetools-frontend/application-config').ConfigOptions}*/const config = {}
For TypeScript files .ts, you can instead import the type directly.
import type { ConfigOptions } from '@commercetools-frontend/application-config';const config: ConfigOptions = {};